The Greenhouse Effect and Its Impact on Climate Change
What is The Greenhouse Effect?

Introduction
In recent decades, the greenhouse effect and climate change have become critical issues of international concern. Climate change results from the abnormal increase in greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere, which has far-reaching consequences and impacts on global life. This article examines the greenhouse effect, its causes and consequences, and its impact on climate change.
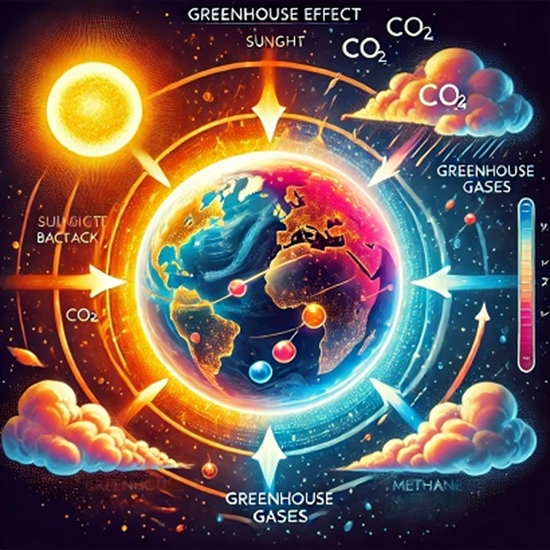
Section 1: Concept and Causes of the Greenhouse Effect
The greenhouse effect refers to the impacts caused by greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere. These gases, including carbon dioxide (CO₂), methane (CH₄), water vapor, nitrous oxide (N₂O), and others, absorb solar energy and prevent its escape into space. This leads to an increase in the average temperature of the Earth's surface. The greenhouse effect occurs due to the presence of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, which can trap solar energy and prevent its reflection into space, thereby increasing the average temperature of the Earth's surface. Human activities such as fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and industrial processes have caused an abnormal increase in these gases, leading to global warming and unwanted climate changes. This phenomenon results in significant changes in weather patterns, loss of biodiversity, and undesirable transformations in ecosystems, which have serious implications for human life and the environment.
Section 2: Consequences of the Greenhouse Effect
The greenhouse effect leads to climate changes, melting glaciers and polar ice, rising sea levels, alterations in precipitation patterns, and an increase in the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events. These climatic changes cause serious disruptions in ecosystems, a decrease in biodiversity, and direct impacts on human health and economic systems.
The greenhouse effect and its changes have extensive implications for global life. These changes include increased temperatures, melting glaciers and polar ice, rising sea levels, shifts in precipitation patterns, and an increase in the frequency and intensity of unstable weather events. For example, rising temperatures lead to more hot days and heatwaves, which can result in heat-related illnesses, reduced agricultural productivity, and decreased outputs in some regions. The melting of glaciers and polar ice contributes to rising sea levels, causing flooding, water contamination, and changes in coastal and marine ecosystems. Changes in precipitation patterns also lead to increased droughts or sudden floods, significantly impacting agriculture, food production, and water resources. Increased frequency and intensity of unstable weather events such as tornadoes and storms cause extensive damage to infrastructure, vital livelihoods, and sustainable development. These consequences underscore the critical need to address the greenhouse effect and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Section 3: Impact of the Greenhouse Effect on Climate Change
The greenhouse effect plays a significant role in amplifying global climate change. Temperature increases, changes in precipitation patterns, increased storm activity, and ocean warming are some of the direct impacts of the greenhouse effect that exacerbate climate changes.
The greenhouse effect plays a crucial role in intensifying global climate change. Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, increased storm activity, and ocean warming are some of the effects of this phenomenon. Increased greenhouse gases result in higher average temperatures, which lead to glacier and polar ice melting, rising sea levels, and changes in precipitation patterns. These changes result in more frequent and intense unstable weather events such as tornadoes, floods, and droughts. Additionally, ocean warming causes alterations in weather patterns across different regions, affecting both aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. These climate changes lead to profound impacts on human and other life forms, necessitating immediate and effective measures to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and address the adverse effects of the greenhouse effect.
Section 4: Addressing the Greenhouse Effect
Addressing the greenhouse effect requires actions such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions, using clean energy sources, protecting forests and natural ecosystems, and raising public awareness about this issue.
Combating the greenhouse effect and its impacts on climate change is of paramount importance. To reduce greenhouse gas emissions, it is essential to utilize clean and renewable energy sources, improve energy efficiency in industry and transportation, increase the use of renewable energy, and enhance energy efficiency at both national and international levels. Additionally, protecting and restoring forests and natural ecosystems, reducing ecosystem degradation, and developing green and environmentally friendly technologies are effective measures against the greenhouse effect. Furthermore, public awareness and continuous education about environmental impacts and the importance of reducing greenhouse gas emissions are crucial. These actions not only contribute to environmental improvement but also enhance human health, reduce economic damages from climate change, and promote community sustainability.
Conclusion
The greenhouse effect is a critical global issue and a significant challenge that requires international collaboration and commitment to address. Climate changes resulting from the greenhouse effect have become one of the most important challenges of the coming centuries, with significant impacts on human life and the global environment.




comment